Virtual Serial Port Windows
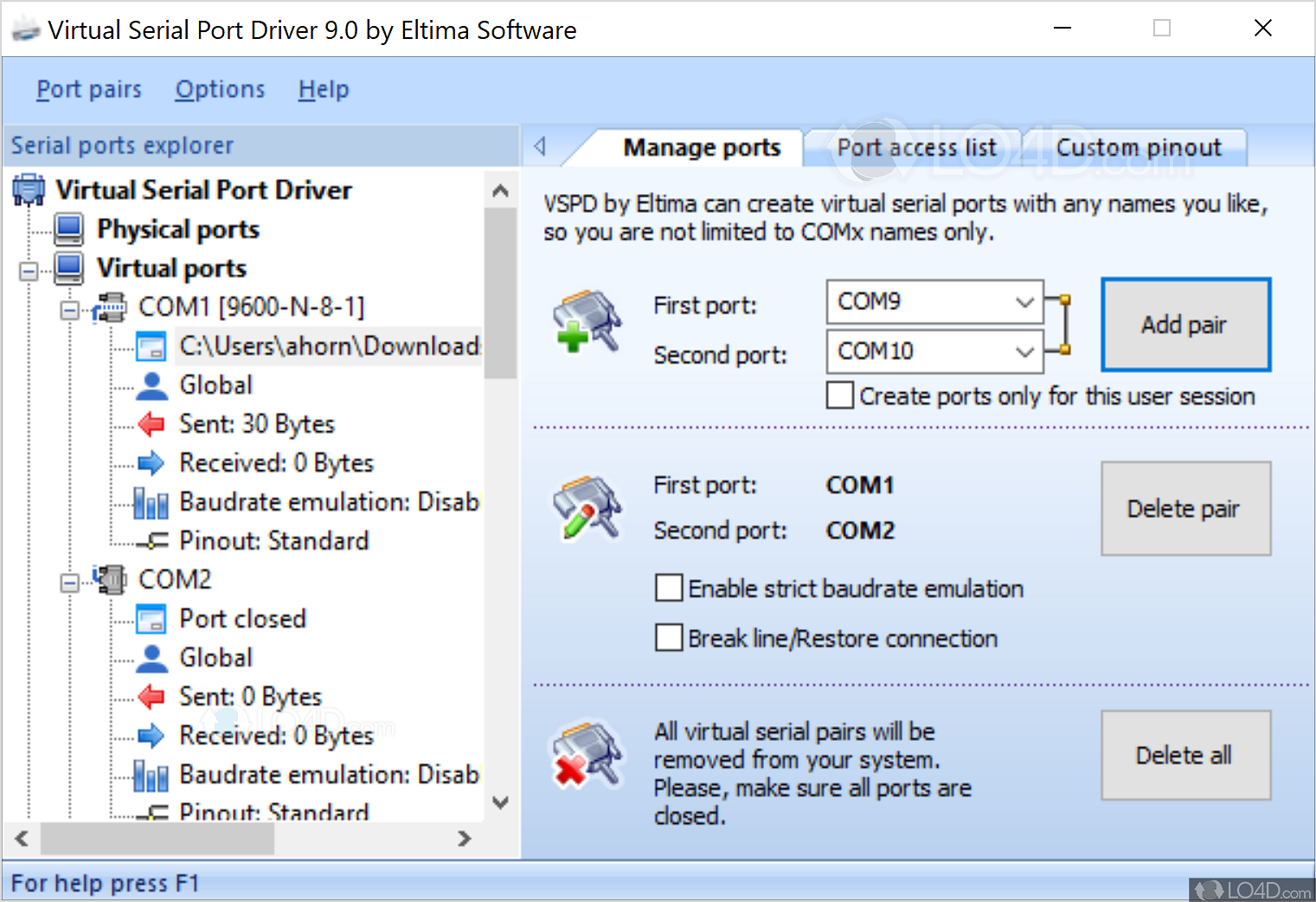
The Null-modem emulator is an open source kernel-mode virtual serial port driver for Windows, available freely under GPL license. The Null-modem emulator allows you to create an unlimited number of virtual COM port Each COM port pair provides two COM ports. May 10, 2021 With Windows kernel technology Virtual Serial Port Driver allows you to create an unlimited number or COM port pairs, fully emulating serial port connections. Virtual Serial Port Emulator Software This software is a perfect virtual serial port emulator works on 32- and 64-bit Windows OS and supports operating systems up to the latest Windows 10. Free Virtual Serial Ports is a software COM port emulation utility for Windows platform. Our freeware virtual serial port tools kit allows you to create virtual COM ports and connect them into pairs using software-based virtual null-modem cables. File Size 6.86 MB. Create Date October 11, 2018. Last Updated February 16, 2021. Description Attached Files. Download the popular Virtual COMM Port Driver for use with NetBurner modules. Add a virtual serial port to your computer and interact with legacy applications or hardware using a modern PC.
Now with support for Windows 7 and originally called Virtual Serial Ports for XP, Virtual Serial Ports is a driver/tool to create virtual ports on your Windows system, making programs and also the OS believe that they are truly serial posts. With these serial ports, applications can communicate with each other and can transfer data via a virtual null-modem.
These is a GUI included with the program.
Features and highlights
- Any number of virtual serial ports pairs can be created
- Virtual serial ports are absolutely the same copies of real ones - applications won't see the difference between real and virtual serial ports
- Virtual serial ports can be controlled directly from your own application via Dynamic Link
- Library supplied with VSPD (for OEM License owners)
- Link between virtual serial ports is much faster than real null-modem cable connection and solely depends on your processor speed (average transfer speed is about 5.5 Mbytes/sec)
- Real serial ports are not occupied - you can even have no real ports in system at all
- Strict baudrate emulation (for Windows NT4/2000/XP/2003/Server 2008/Vista/Windows 7)
Virtual Serial Port Driver 9.0 on 32-bit and 64-bit PCs
This download is licensed as shareware for the Windows operating system from drivers and can be used as a free trial until the trial period ends (after 14 days). The Virtual Serial Ports Driver XP 9.0 demo is available to all software users as a free download with potential restrictions and is not necessarily the full version of this software.- Virtual Serial Port Driver Download
A virtual port (VPort) is data object that represents an internal port on the NIC switch of a network adapter that supports single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV). Each NIC switch has the following ports for network connectivity:
One external physical port for connectivity to the external physical network.
One or more internal VPorts which are connected to the PCI Express Physical Function (PF) or virtual functions (VFs).
The PF is attached to the Hyper-V parent partition and is exposed as a virtual network adapter in the management operating system that runs in that partition.
A VF is attached to the Hyper-V child partition and is exposed as a virtual network adapter in the guest operating system that runs in that partition.
The NIC switch bridges network traffic from the physical port to one or more VPorts. This provides virtualized access to the underlying physical network interface.
Each VPort has a unique identifier (VPortId) that is unique for the NIC switch on the network adapter. A default VPort always exists on the default NIC switch and can never be deleted. The default VPort has the VPortId of NDIS_DEFAULT_VPORT_ID.

When the PF miniport driver handles an object identifier (OID) method request of OID_NIC_SWITCH_CREATE_SWITCH, it creates the NIC switch and the default VPort for that switch. The default VPort is always attached to the PF and is always in an operational state.
Nondefault VPorts are created through OID method requests of OID_NIC_SWITCH_CREATE_VPORT. Only one nondefault VPort can be attached to a VF. Once attached, the default is in an operational state. One or more nondefault VPorts can also be created and attached to the PF. These VPorts are nonoperational when created and can become operational through an OID set request of OID_NIC_SWITCH_VPORT_PARAMETERS.
Note After a VPort becomes operational, it can only become nonoperational when it is deleted through an OID request of OID_NIC_SWITCH_DELETE_VPORT.
Each VPort has one or more hardware queue pairs associated with it for receiving and transmitting packets. The default queue pair on the network adapter is reserved for use by the default VPort. Queue pairs for nondefault VPorts are allocated and assigned when the VPort is created through the OID_NIC_SWITCH_CREATE_VPORT request.
Nondefault VPorts are created and configured through OID method requests of OID_NIC_SWITCH_CREATE_VPORT. The default VPort and nondefault VPorts are reconfigured through OID set requests of OID_NIC_SWITCH_VPORT_PARAMETERS. Each OID request contains an NDIS_NIC_SWITCH_VPORT_PARAMETERS structure that specifies the following configuration parameters:
The PCIe function to which the VPort is attached.
Each VPort can be either attached to the PF or with a VF at any time. After the VPort is created and attached to a PCIe function, the attachment cannot be dynamically changed to another PCIe function.
Note The default VPort is always attached to the PF on the network adapter.
Starting with NDIS 6.30 in Windows Server 2012, only one nondefault VPort can be attached to a VF. However, multiple nondefault VPorts along with the default VPort can be attached to the PF.
The number of hardware queue pairs that are assigned to a VPort.
Each VPort has a set of hardware queue pairs that are available to it. Each queue pair consists of a separate transmit and receive queue on the network adapter.
Queue pairs are limited resources on the network adapter. The total number of queue pairs reserved for use by the default and nondefault VPorts is specified when the NIC switch is created. This allows the number of queue pairs that are assigned to the default VPort to differ from the nondefault VPorts.
Each nondefault VPort can be configured to have a different number of queue pairs. This is known as asymmetric allocation of queue pairs. If the NIC does not allow for such an asymmetric allocation, each nondefault VPort is configured to have equal number of queue pairs. This is known as symmetric allocation of queue pairs. For more information, see Symmetric and Asymmetric Assignment of Queue Pairs.
Note The PF miniport driver reports on whether it supports asymmetric allocation of queue pairs during MiniportInitializeEx. For more information, see Initializing a PF Miniport Driver.
The number of queue pairs assigned to each VPort is not changed dynamically. The number of queue pairs assigned to a VPort cannot be changed after the VPort has been created.
Virtual Serial Port Windows 10 Free
Note One or more queue pairs assigned to the nondefault VPorts can be used for receive side scaling (RSS) by the VF miniport driver that runs in the guest operating system.
Interrupt moderation parameters for the VPort.
Different interrupt moderation types can be specified for different VPorts. This allows the virtualization stack to control the number of interrupts generated by a particular VPort.
In addition to configuration parameters, overlying drivers can configure receive filters for each VPort by issuing OID method requests of OID_RECEIVE_FILTER_SET_FILTER. The NIC switch performs the specified receive filtering on a VPort basis.
Receive filters parameters for VPorts include packet filtering conditions, such as a list of media access control (MAC) addresses and the virtual LAN (VLAN) identifiers. Filters for MAC addresses and VLAN identifiers are always specified together in the NDIS_RECEIVE_FILTER_PARAMETERS associated with the OID_RECEIVE_FILTER_SET_FILTER request. The NIC switch must filter incoming packets to the switch whose destination MAC address and VLAN identifier matches any receive filter condition that was set on the VPort. The NIC switch filters packets received from either another VPort or from the external physical port. If the packet matches a filter, the NIC switch must forward it to the VPort.
Multiple MAC address and VLAN identifier pairs may be set on the VPort. If only a MAC address is set, the receive filter specifies that the VPort should receive packets that match the following condition:
The packet's destination MAC address matches the filter's MAC address.
The packet has a VLAN tag or (if a VLAN tag is present) a VLAN identifier of zero.
Virtual Com Port Windows 10 Open Source
Nondefault VPorts are deleted through OID set requests of OID_NIC_SWITCH_DELETE_VPORT. The default VPort is only deleted when the NIC switch is deleted through an OID set request of OID_NIC_SWITCH_DELETE_SWITCH.